Assets attributable to sustainable funds reach $1.4 trillion in October, expanding by 24% since September as mutual fund re-brandings continue to gain momentum
Sustainable investment funds(1), including mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and exchange-traded notes (ETNs) reached $1.4 trillion in assets under management at the end of October 2019, adding $273.8 billion since September or an increase of 23.9%. Refer to Chart 1. This was the 8th monthly gain so far this year and second only in magnitude to the increase achieved last month. In both instances the sizable gains in net assets are sourced to fund re-brandings. Last month, J.P. Morgan re-branded 36 funds/163 share classes valued at $359.8 billion by amending its fund prospectuses to reflect that as part of its security selection strategy the firm also evaluates whether environmental, social and governance factors could have material negative or positive impacts on the cash flows or risk profiles of many companies in the universe in which the applicable funds may invest. In October, four fund companies re-branded a total of 84 funds managing $256.2 billion in total net assets. Of these, MFS alone transformed 67 funds, 541 share classes, and a combined total of $244.9 billion in assets under management. In addition, market appreciation contributed an estimated $13.1 billion to the segment’s assets, bolstered by domestic and foreign stock market gains in October. Estimated net cash flows came in at $4.45 billion, or an increase of 0.4% relative to the previous month’s total net assets–the third best monthly gain this year. Several new funds were launched in October, including an additional green bond fund and several fund closures were also reported.
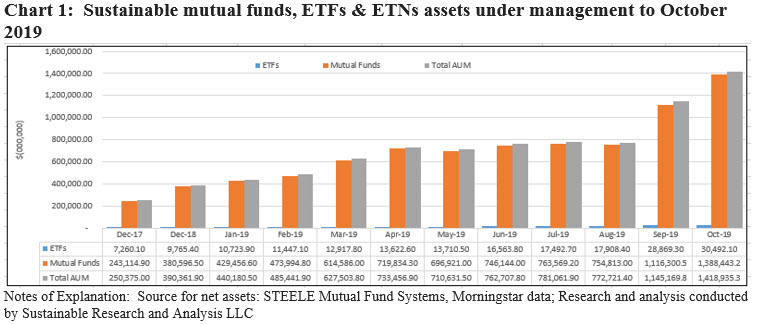
Since the start of the year, sustainable fund assets have expanded by $1.03 trillion, from $390.4 billion at December 31, 2018, or an increase of 263%. In the process, the profile of assets linked to sustainable investing strategies has changed significantly.
Fund re-brandings add $256.2 billion in October, second only to last month’s $368.7 billion
Four firms re-branded existing funds this month, including MFS, Brown Advisory, Eaton Vance and Morgan Stanley. Two of these firms, namely MFS and Eaton Vance, are making an appearance in the sustainable investing sphere for the first time. Refer to Table 1.
MFS, ranked as one of the world’s top 100 asset managers, re-branded a total of 67 funds/541 share classes covering long-term investment funds that extend from core equity, US and international funds, sector funds, taxable and municipal bond funds as well as alternative and commodity funds. Effective October 31, 2019, MFS amended the Principle Investment Strategies section of its relevant fund prospectuses to reflect that “MFS may also consider environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in its fundamental investment analysis.” While Eaton Vance owns Calvert Research and Management, a pioneer in sustainable investing, the re-branding of three existing NextShares products (a new type of actively managed ETF) is the first direct sustainable investment entry managed by the parent company Similar to MFS, Eaton Vance amended each NextShares prospectus by adopting the following language: “As part of the research process, portfolio management may consider financially material environmental, social and governance (“ESG”) factors. Such factors, alongside other relevant factors, may be taken into account in the Fund’s securities selection process.” By way of contrast, funds offered by Calvert explicitly integrate ESG factors.
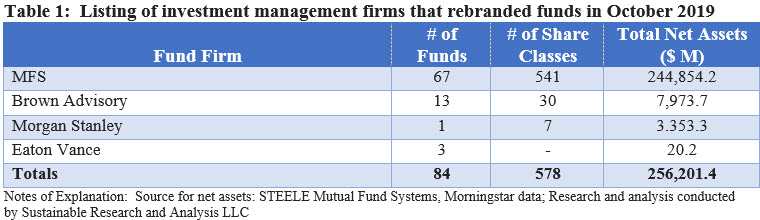
The amendment language adopted by MFS and Eaton Vance contrasts to the amendments adopted by Brown Advisory and Morgan Stanley, each of which signals a more definitive commitment to consider ESG factors. In the case of Brown Advisory, the prospectus amendments read as follows: “The Adviser assesses a company’s Environmental, Social and Governance (“ESG”) profile through conducting ESG research and leveraging engagement when appropriate through dialogue with company management teams as part of its fundamental due diligence process. The Adviser views ESG characteristics as material to fundamentals and seeks to understand their impact on companies in which the Fund may invest.” As for Morgan Stanley, which re-branded a prime money market fund, the prospectus amendment notes, in part, that the fund’s “investment process incorporates information about ESG issues, using a proprietary ESG scoring methodology that combines third-party ESG data with proprietary views, to explicitly consider the risks and opportunities ESG factors pose to money market instruments.”
Recent fund re-brandings transform profile of the sustainable funds universe
In just the last two months, the profile of the sustainable funds universe has been transformed in at least two material ways. First, the distribution of sustainable fund assets across various asset classes is now more closely aligned with the combined assets of the broader mutual fund and ETF universe. In particular, the addition by J.P. Morgan last month of money market funds that integrate ESG shifted the percentage of sustainable assets invested in money market funds from nearly 0.0% to 19.5% of combined assets at the end of October. This compares to 14.2% sourced to money market funds in the broader universe of mutual funds and ETFs(2) . At the same time, sustainable fixed income funds, including taxable and municipal bond funds, now account for 19.6% of net assets versus 22.2% across the combined assets of mutual funds and ETFs. This compares to about 17% in August and 6.6% since the start of the year. Refer to Chart 2.
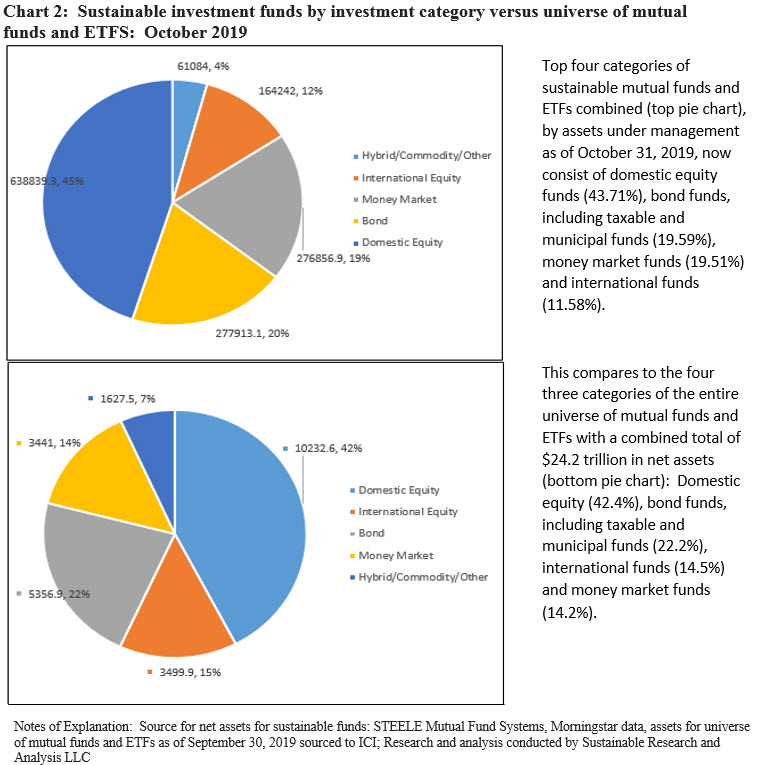
Another significant shift is the advancement and now clear dominance of ESG integration as the leading approach/strategy that’s either applied exclusively or in combination with other strategies, for example, such as negative screening (exclusions), impact or shareholder/bondholder engagement. This contrasts with the tilt toward negative screening (exclusions) that dominated sustainable investing mutual funds and ETF up to just a few months ago.
Four new ESG funds were launched in October, including the first municipal green bond fund; Two fund closings announced
In addition to introducing several new share classes, four fund groups launched new sustainable investment funds during the month of October. Refer to Table 2.
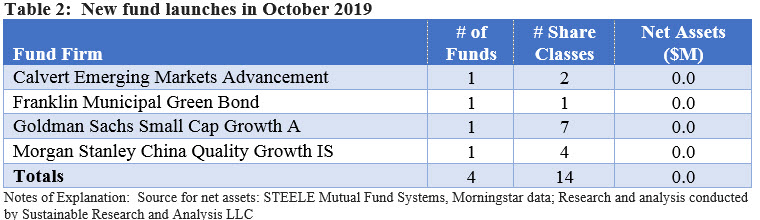
One of these new funds is the Franklin Municipal Green Bond Fund. The launch of this fund brings to seven the number of green bond funds, either mutual funds or ETFs, currently offered. This fund, however, is the first municipal fund offering. The fund intends to invest at least 80% of its net assets in municipal green bonds, defined by Franklin as bonds that promote environmental sustainability.
Also in October, two fund firms proceeded to close two mutual funds. These include the $32 million Invesco OFI Pictet Global Environmental Solutions Fund and the $29.0 million Franklin Templeton Templeton Global Currency Fund.
Largest Fund Groups: Top 20 sustainable fund groups now account for $1.3 trillion in assets as concentration intensifies
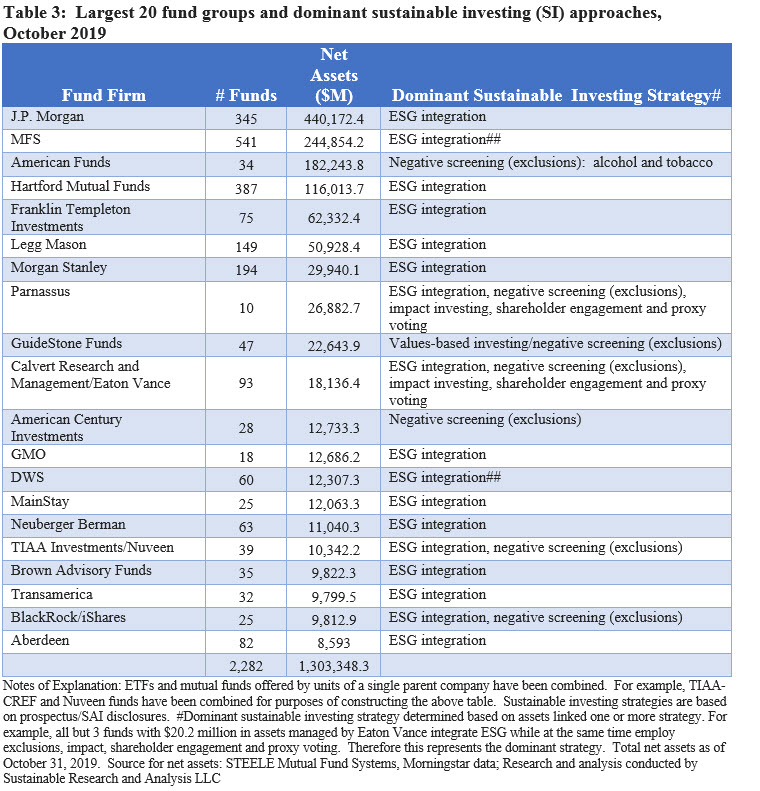
With the addition of MFS, a total of 150 fund groups now offer sustainable mutual funds and ETFs as of the end of October 2019. Of these, the largest 20 fund groups now account for $1,303.3 million or just about 92% of net assets versus 91.4% last month and 87.9% the month previous. On the basis of their re-brandings, both MFS and Brown Advisory now rank within the list of the top 20 fund firms offering sustainable funds while two firms that were previously ranked in the top 20 have been displaced. These include Dimensional Fund Advisors (DFA) and Jensen. These two firms offer a total of 12 funds with $16.6 billion in assets managed pursuant to various sustainable strategies. Refer to Table 3.
The top three firms on the basis of assets under management include J.P. Morgan, MFS and American Funds. Together, these firms account for 61% of the segment’s total assets under management. The displacement of American Funds, which had, to August of this year, been ranked as the lead sustainable fund firm on the basis of assets under management by applying a negative screening approach for alcohol and tobacco products to just two of its fund offerings, combined with the re-brandings that have taken place over the previous two months, have produced a shift in the profile of strategies employed by sustainable mutual funds and ETFs. ESG integration, either exclusively or in combination, has now eclipsed negative screening (exclusions) as the more common approach in the segment. But as noted earlier, ESG integration based on prospectus disclosures, methodological considerations aside, seems to be evolving along two paths. One consists of fund firms and funds that have made a definitive commitment to consider ESG factors while the other consists of fund firms like MFS that “may” account for ESG factors. These varying approaches will likely add to increased scrutiny and calls for improved definitions and disclosures in the future.
(1) While the definition of sustainable investing continues to evolve, today it refers to a range of five overarching investing approaches or strategies that encompass: values-based investing, negative screening (exclusions), thematic and impact investing, ESG integration and shareholder/bondholder engagement and proxy voting. These are not mutually exclusive.
(2) The allocation of mutual fund and ETF assets across asset classes is based on ICI data as of September 30, 2019, the latest available.